Scaffolding planks are very common on construction sites, workers walk on them, but in fact, there are many materials and types of scaffolding planks. How should we choose? Should there be corresponding regulations when using them?
Please read this article, I believe you will have a comprehensive understanding of scaffolding planks.
What is Scaffold Planks?
Scaffold planks are an important part of scaffolding systems, they are platforms or walkways that are built for workers to access higher areas in order for them to carry out building construction, maintenance or repair work in higher areas.
You can use scaffolding planks in a wide range of scaffolding systems such as ringlock scaffolding, cuplock scaffolding, kwikstage scaffolding, mobile towers and many more, these planks are usually made from high-quality materials such as aluminium, steel or wood and are designed to provide a stable and safe platform for workers to perform their tasks at height.
Types of Scaffold Planks
Wood Planks
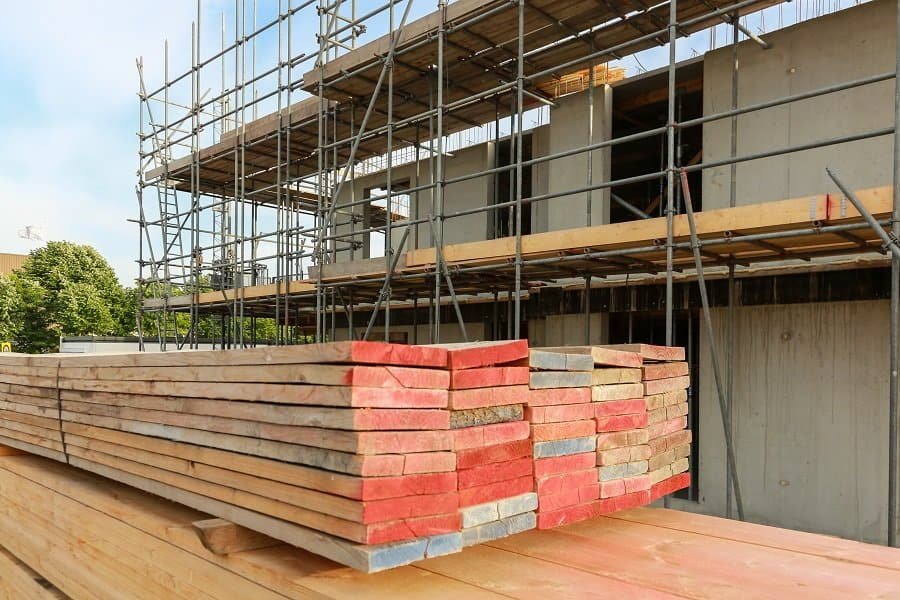
The wooden scaffold plank is the most common type of scaffold plank, usually made of fir or pine wood. The thickness of the wooden scaffold plank is usually greater than 50mm, with a width of 200–250 mm and a length of 3–6 m.
To prevent damage to the ends of the scaffold plank during use and extend its lifespan, it can be tightly bound with iron wire at a distance of 80mm from each end or wrapped with iron sheet with a thickness of 0.4–0.6 mm.


Wooden scaffold planks are commonly used for bamboo and wooden scaffolding, cuplock scaffolding, and independent inclined ramps with heavy loads. They are less commonly used for mobile scaffolding, various types of tool scaffolding, and portal scaffolding.
The characteristics of wooden scaffold planks are their wide range of uses, simple installation methods, and easy disassembly. They provide a good foot feel for construction workers during use.
However, in some countries, due to the implementation of environmental protection policies, the availability of raw materials has decreased relatively, resulting in a decreasing trend in usage.






Steel Planks
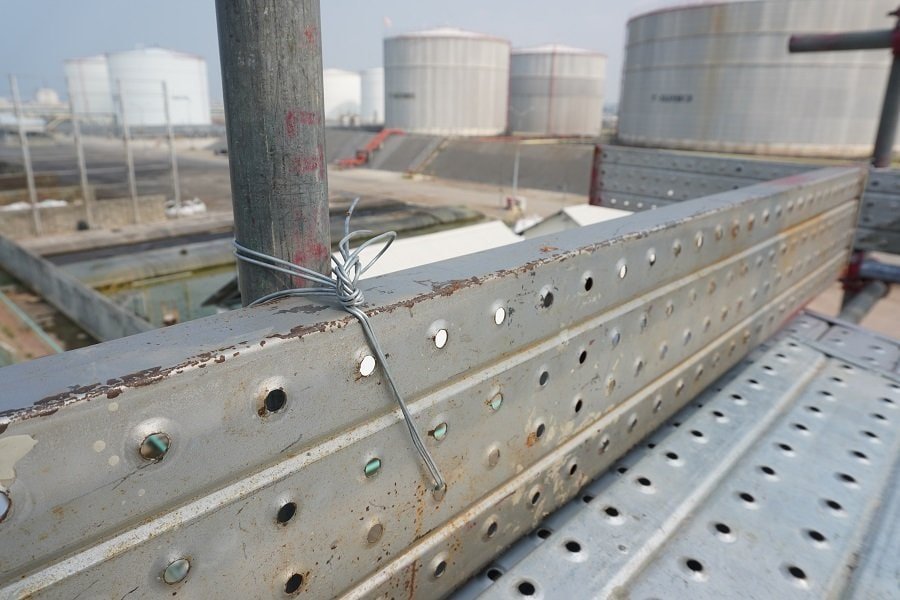
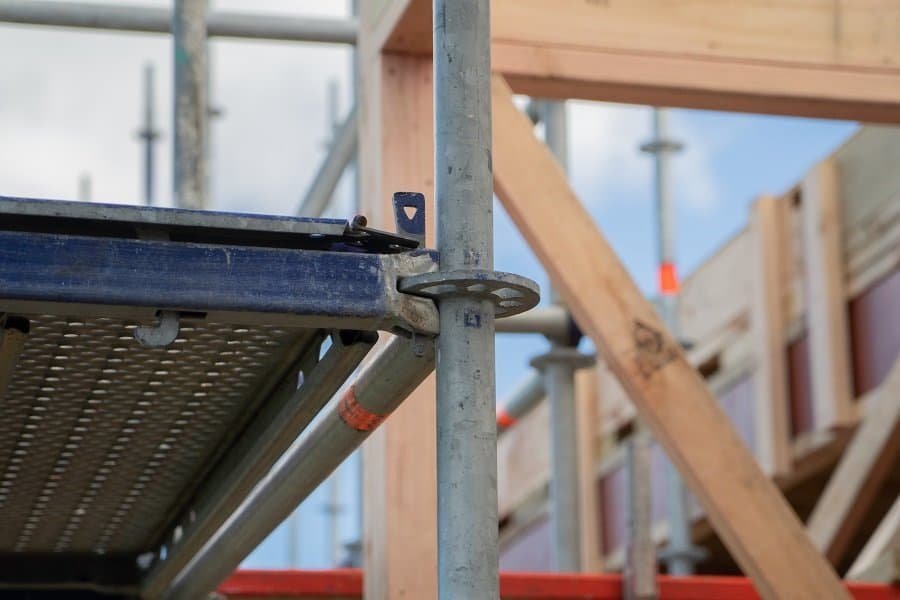
Steel scaffold plank is also a common type of scaffold plank, generally made of Q195~Q235 steel as raw material. It can be selected with galvanized or non-galvanized board according to needs.
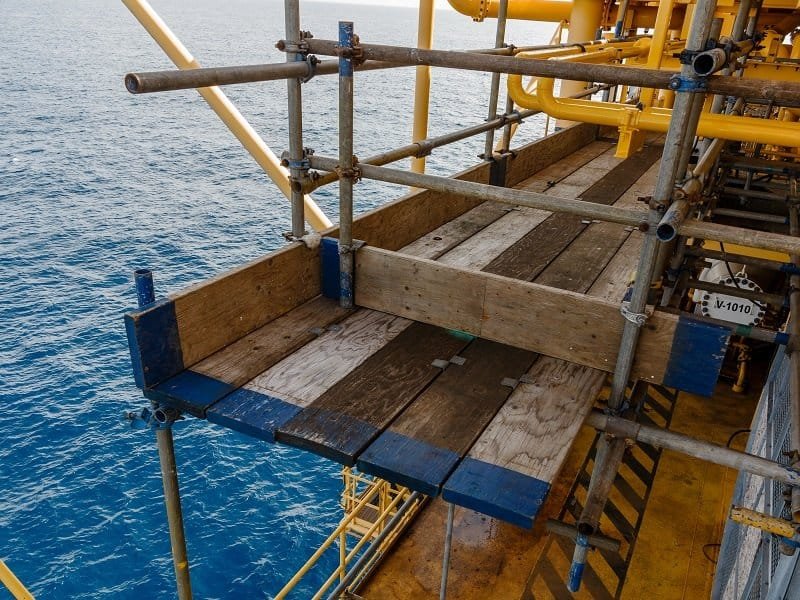
Steel scaffold planks are flame retardant, sturdy, durable, and corrosion resistant. You can watch them on ringlock scaffolding, kwikstage scaffolding, scaffold tower, etc.
They are usually used in heavy-duty applications or in fields with high fire safety requirements, such as the petrochemical, oil, and gas industries.


Aluminum Plank
Aluminum scaffold planks are a type of scaffolding component made of aluminum alloy. This material means that they will not rust and can be used for a long time, with a lifespan far exceeding that of wooden scaffold planks.Additionally, they are lighter, sturdier, more durable, and safer than wood. They can be quickly assembled and conveniently transported. Aluminum planks are slightly lighter than metal planks, but they are not as strong or weather-resistant.They are commonly used in indoor and outdoor decoration, cleaning, maintenance of exhibition halls, and in applications where weight requirements are high, such as in high-rise buildings.
Plastic Plank
Plastic scaffold boards are an innovative type of scaffolding board made from a recyclable polymer composite material. This is a clean material that can be recycled. Compared to traditional wood and steel, it has many obvious advantages: lightweight, durable, sturdy, easy to clean and maintain.However, it has a lower resistance to extreme temperatures and it can’t withstand large impacts. And this is new product, people tend to prefer using traditional wooden or steel scaffold boards.
Advantage and Disadvantage of Scaffold Planks
In the previous section we introduced you to four different materials for scaffold planks, with wooden and steel being the two most widely used on the market today, and not many using aluminium or plastic. So for these two most widely used scaffold planks, what are their advantages and disadvantages? I believe you can get the answer in this part.

Wooden Scaffold Planks
- Advantages
Lightweight: wood is relatively lightweight and can be carried and lifted by one person, making it easier to handle and transport.
Sound-absorbing: wood scaffold boards have a natural sound-absorbing effect.
High friction surface: provides good grip and reduces the risk of slipping.
Cost-effective: wood is a relatively cheap raw material and is often an affordable option.
Disadvantages
High maintenance costs: proper inspection and maintenance must be carried out frequently, and the sheets must be stored away from the natural environment to prevent warping and rotting.
Water absorption: even after treatment, they absorb water, become heavier and may reduce weight limits
Relatively flammable: highly flammable unless chemically treated, and treatment reduces strength.
Easily loosened: workers walking on them can cause bouncing and shifting.

Steel Scaffold Planks
- Advantages
Load-bearing capacity: Steel scaffolding planks have strong load-bearing capacity and can support heavy equipment, tools, and workers, making them suitable for heavy-duty projects.
High corrosion resistance: They can resist moisture and extreme weather conditions, making them durable and suitable for multiple projects without frequent replacement.
Fire-resistant: They are highly suitable for high-temperature operations, such as in factories with a high risk of fire.
Easy maintenance: Steel scaffolding boards require minimal maintenance and are easy to clean.
Long service life: Although the initial cost of steel scaffolding boards may be higher than other materials, such as wood, they can save costs in the long run. They are durable, have low maintenance requirements, and have a longer lifespan, resulting in fewer replacements and ultimately reducing the overall project cost.
Disadvantages
High cost: Compared to other materials, the price of steel scaffolding is relatively high.
Weight: Due to being made of steel, the weight of steel scaffolding is heavier compared to products of the same specifications.
Transportation: Due to the weight, the corresponding transportation cost is also relatively high.
Difference Between Steel Scaffold Planks And Wooden Scaffold Planks
Which One Do You To Choose?
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of wood and steel planks does not mean knowing how we should go about choosing them, when choosing scaffolding boards you need to consider the points of greatest concern for your project, let’s see what are worth our attention!

- Cost
Wooden scaffold planks: They are usually cheaper than steel planks, making them an economical choice for small projects or short-term use.
Steel scaffolding planks: steel is a metal material and steel planks are more expensive. In addition, the production process for steel scaffolding planks is relatively complex, requiring multiple steps, making the cost relatively higher.

- Maintenance
Wooden scaffold planks: wooden planks may be more susceptible to damage from weather conditions, moisture, and wear and tear, and you may need to replace them more frequently, as well as needing regular treatments for corrosion and moisture resistance.
Steel scaffold planks: generally do not require special maintenance treatments as steel has better corrosion and weather resistance.
Transport
Wooden scaffolding planks: They are lightweight and easy to handle and transport. However, as wood is susceptible to moisture and deformation, you need to take special care to protect it during transport.
Steel scaffolding planks: weigh more and are relatively difficult to handle and transport. However, steel has high strength and stability, so it is less likely to be deformed or damaged during transport.

- Lifetime
Wooden scaffold planks: the wood material is relatively easy to deteriorate and has a shorter service life.
Steel scaffold planks: they can withstand harsh weather conditions and are not prone to warping, cracking or rotting, so they have a longer service life.
- Load-bearing
Wooden scaffold planks: They have a relatively low load-bearing capacity because wood is not as strong or stable as steel and is more suitable for light work or temporary structures.
Steel scaffold planks: compared to timber planks, steel planks have a higher load-bearing capacity and can support heavier loads and multiple workers at the same time. This advantage increases efficiency and productivity on construction sites, allowing projects to be completed faster.
In contrast, steel scaffold planks are more durable and long-lasting and are suitable for heavy-duty and long-term projects.

Maintenance and Storage
- You Need to Clean and preserve scaffold planks
Removing dirt, debris, and contaminants.
Scaffold planks should be cleaned on time during use, and harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners that can damage the wood should be avoided to prolong the life of the planks for easy reuse.
- Applying protective coatings or treatments
If you want to prolong the use, some will coat the scaffold boards with a protective coating, but be aware that this needs to be confirmed with the merchant at the time of purchase. For example, wood scaffold boards are coated with a corrosion-resistant paint, or you can choose steel scaffold boards that have been hot-dip galvanized.
- Proper storage of scaffold boards
You need to store boards in a dry and secure location, protecting them from moisture and physical damage.
Take care to store wooden scaffolding in a dry and well-ventilated area, preferably with the boards stored in a covered area to protect them from direct sunlight, rain, and other weather elements to prevent moisture and physical damage to the planks.
OSHA Requirements For Scaffolding Planks
The full name of OSHA is Occupational Safety and Health Administration, established in 1970. It is a national public health agency under the U.S. Department of Labor. Its goal is to provide workers with a safe and healthy working environment and conditions and reduce the rate of work-related injuries through the development and enforcement of standards, as well as providing training, education, and assistance, among other efforts.
Specific requirements for scaffold boards are set by OSHA:
- The wood used for scaffold boards should meet quality requirements and follow recognized wood-grading associations. Scaffold boards labeled “OSHA Conformed” generally comply with the regulations.
- The wood should be in good condition without cracks, and scaffold boards with paint or concrete are not allowed to be used because the condition inside cannot be determined by appearance.
- The longer the span of the scaffold board, the greater the deflection (bending), resulting in a smaller load capacity. Therefore, when purchasing scaffold boards, the length, deflection, and load capacity of the boards should be considered, and the appropriate length and thickness should be selected.
For specific regulations regarding span and deflection, please refer to this link:
https://www.osha.gov/etools/scaffolding/planking
It is important for you to note that these are general guidelines, and specific requirements may vary depending on the specific situation and jurisdiction. It is recommended to always consult local regulations or qualified professionals to obtain the latest detailed information regarding scaffold board requirements.
Scaffold Boards Safety Tips
- Proper installation of scaffold boards
- Ensuring boards are securely fastened
- Regular inspections for any damage or defects
Inspect scaffold planks before and after each use for any signs of damage such as cracks, splits or warping. If any damage is found, take the scaffold planks out of service and replace them.
- Weight capacity and load distribution
- Understanding the weight limits of scaffold boards
- Distributing loads evenly to prevent overloading
Do not exceed the maximum load capacity specified by the scaffold plank manufacturer. Overloading can weaken the planks and increase the risk of accidents or collapse.
Common Misuses of Scaffold Planks
Using non-certified boards (e.g., lumberyard wood).
Overloading planks beyond their rated SWL.
Painting timber planks (hides cracks and prevents inspection).
Improper stacking or uneven placement, creating trip hazards.
A scaffold plank is not “just a board.” Treating it casually is a recipe for accidents.
Conclusion
In this article, we delve into various aspects of scaffold planks, including their types, regulations, maintenance and storage. Whether you are a construction worker or someone interested in the construction industry, we hope this article has provided you with valuable information about scaffold planks.
If you have any further questions about scaffold planks or need professional advice, our company is more than happy to help. Please feel free to contact us and our team will be on hand to support you.
FAQ
What If I Require A Scaffold Plank In A Different Length or Width?
If you need scaffolding planks in different lengths or widths, we can customize them according to your requirements. Please let us know your specific needs and we will do our best to provide you with a satisfactory service.
Are Scaffold Boards Made of Pine?
Scaffold boards can be made from a variety of materials including pine. Pine is a softwood commonly used for temporary structures and low to medium use. It can be suitable for some scaffolding applications, but may not have the strength and durability needed for more demanding tasks. Other materials commonly used for scaffold boards include steel, aluminium and wood composites. These materials offer greater strength, durability and corrosion resistance, making them more suitable for heavy or long-term use. When choosing a scaffold board material, it is important to consider the intended use, the environment and the durability required.
What is The Lifespan of a Scaffold Board?
The service life of scaffold boards may vary depending on a number of factors, including the material they are made of, the quality of the manufacturing process, the conditions of use and maintenance. If you want to know more details, please feel free to contact us!
Are Scaffolding Boards Better Than Decking?
Scaffold boards and decking boards are different materials with different uses and properties. Therefore, it is not possible to directly compare their “merits”.
Scaffold boards are usually made from steel, aluminium or timber and are designed for temporary support and construction, they are often used on construction sites such as building refurbishment or repairs to provide a stable platform for workers and materials.
Decorative boards are usually made of wood or composite materials and are designed for permanent outdoor use. Deck planks are typically used for patios, decks, or other outdoor living spaces to create a safe, aesthetically pleasing surface.
How wide should scaffold planks be?
Typically 225 mm (9 inches), but varies depending on scaffold system.