Workers face many risks when working at heights, with falls being the most common. In response to this situation, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) mandates that employers provide one of three safety solutions for employees: guardrail systems, safety net systems, or personal fall arrest systems.
Among these options, safety nets are widely favored by employers as a construction safety product. This article provides detailed information about safety nets, aiming to address all your questions regarding this safety solution.
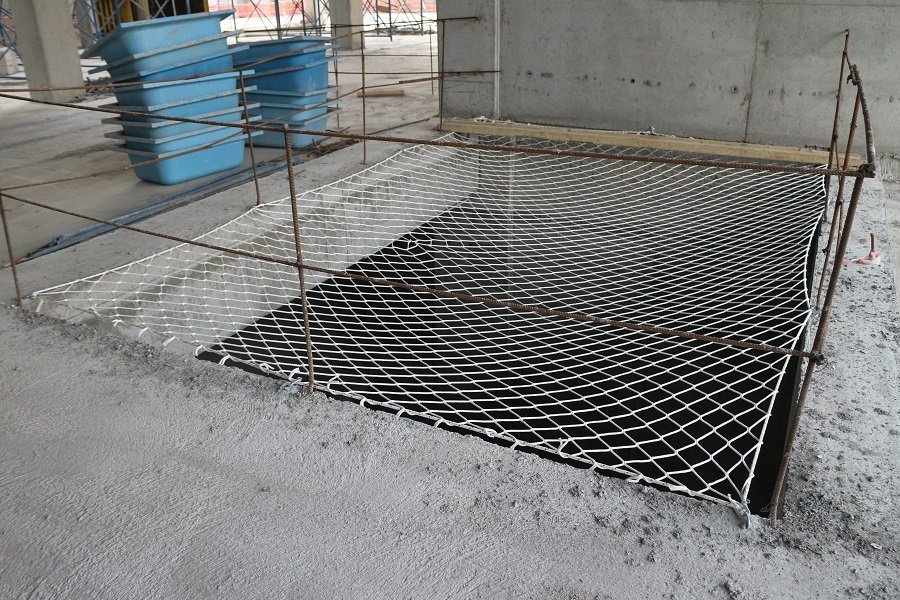
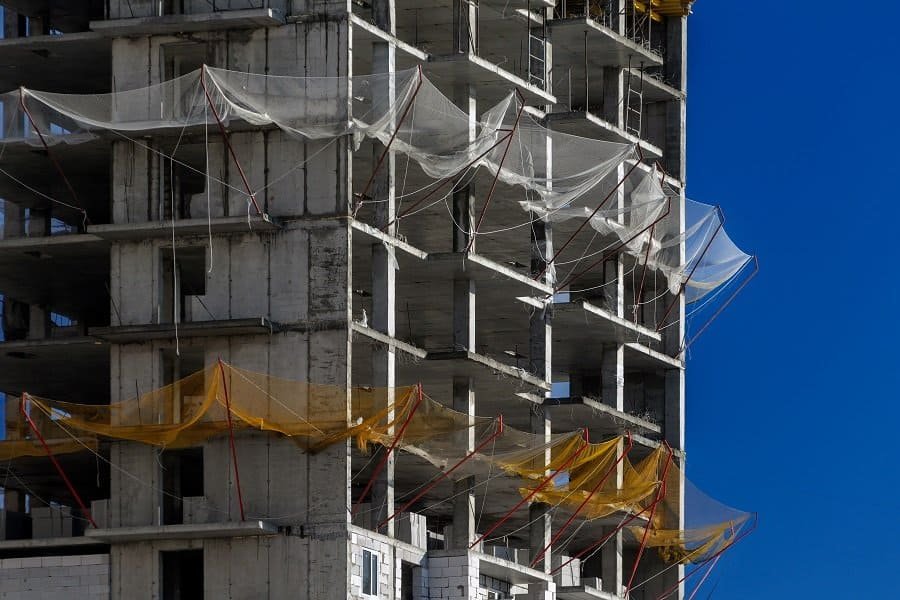


What is Safety Net in Construction?
Falls from heights are one of the leading causes of death and serious injury in the construction industry. The primary reason for using safety nets is to protect the lives and health of construction workers.
Safety nets, sometimes referred to as “vertical safety nets” or “horizontal safety nets,” are support nets erected on the interior and exterior of buildings under construction. They serve as collective fall arrest devices and are typically used at heights of 10 meters or more. Safety nets can slow down or dissipate the impact energy of falling personnel or debris during construction, thereby preventing accidents and saving lives.
Why Using Safety Net is a must During Construction?
Regulation Requirement
Many countries have strict workplace safety regulations and standards, including requirements for fall prevention on construction sites.
In the UK, the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) issues the Health and Safety at Work Act, which mandates taking all reasonably practicable measures to prevent harm to employees.
According to regulations from the United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), employers must provide fall protection when workers are working at heights higher than six feet above a lower level or near hazardous machinery or equipment.
Using safety nets helps ensure compliance with these regulations, aiding in avoiding fines, legal issues, and project delays.

- Fall Prevention
Safety nets are a vital layer of protection against falls from heights. Construction sites often involve working at elevated levels, such as on scaffolding, roofs, or upper floors of buildings. Safety nets serve as a barrier, catching workers who may fall and preventing or minimizing injuries. Safety nets provide peace of mind for workers, allowing them to focus on their tasks without worrying about the risk of falling.
- Save Cost
Although purchasing safety nets requires an initial investment, in the long run, they can save costs money. Preventing worker injuries can reduce medical expenses, workers’ compensation claims, and potential legal fees. Additionally, avoiding accidents helps maintain productivity and avoid project delays. By prioritizing safety measures like safety nets, companies can not only protect their workers but also safeguard their bottom line and reputation.
Types of safety net in construction
According to the number of layers:
- A single-layer safety net
This type of safety net consists of only one layer of netting and is suitable for general safety protection needs.
- Double-layer safety net
Features two layers of netting, providing better safety protection, especially in situations requiring higher strength or durability.
- Triple-layer safety net
With three layers of netting, it offers even higher-strength protection.
1-layer safety net

2-layer saferty

3-layer safety
According to the weaving method:
- Knotted safety net
Each node of this net is secured with a knot or fastener during production, enhancing the overall solidity and stability of the net, making it more durable. However, due to the knots, it may be slightly heavier.
- Knotless safety net
In contrast to knotted nets, knotless nets are woven without the use of knots or fasteners.


According to the mesh shape:
- Square (Q) mesh
Comprises square-shaped mesh, providing a stable structure and facilitating easy observation and inspection for damage or breakage.
- Diamond (D) mesh
Consists of diamond-shaped mesh, offering a compact structure and effectively preventing people or objects from passing through smaller gaps.
According to the direction of use:
- Vertical Safety Net
Installed in a vertical orientation, enveloping the building like a protective shield, and used to prevent people or objects from falling.
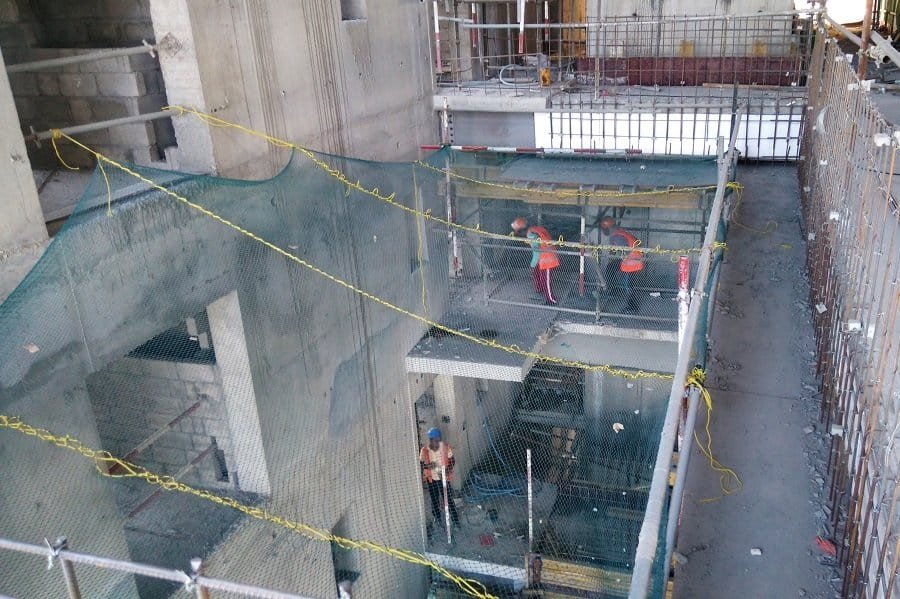


- Horizontal Safety Net
Installed horizontally, these safety nets prevent people or objects from falling from heights.
What are safety nets made of?
Safety nets can be made of various materials, each with its own characteristics and suitability for different applications:
Nylon: Nylon safety nets are popular due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, abrasion resistance, and elasticity. They can absorb the impact of falls and are commonly used in heavy-duty applications.
Polypropylene (PP): Polypropylene safety nets are lightweight, weather-resistant, and cost-effective. They have good tensile strength and are suitable for use in various construction environments.
Polyethylene (PE): Polyethylene safety nets are known for their flexibility, UV resistance, and chemical resistance. They are often used in outdoor applications as they can withstand exposure to sunlight and harsh weather conditions.
Each material has its advantages and may be chosen based on factors such as the specific requirements of the construction project, environmental conditions, and budget considerations.
Applications of safety nets in construction
Roofs: Roofs are one of the most common applications of safety nets in construction. Safety nets are installed beneath the roof structure to protect workers engaged in roofing activities. They provide a safety barrier, minimizing the risk of falls from sloped or flat roofs.
Around Scaffolding: Vertical construction safety nets are typically used around scaffolding structures to provide fall protection for workers accessing elevated platforms. They help prevent falls from scaffolding platforms or working levels.
Bridge Construction: Safety nets are utilized in bridge construction projects to protect workers working on elevated sections of bridges or overpasses. Installed beneath the bridge structure, safety nets catch workers in the event of falls.
High-Rise Buildings: Safety nets are essential for protecting workers during high-rise construction projects. They are installed at multiple levels of the building under construction, providing fall protection for workers on upper floors or exterior facades.
Building Openings: During construction, there are often openings in the structure posing significant fall hazards. Safety nets are installed to prevent workers or debris from falling through these openings.
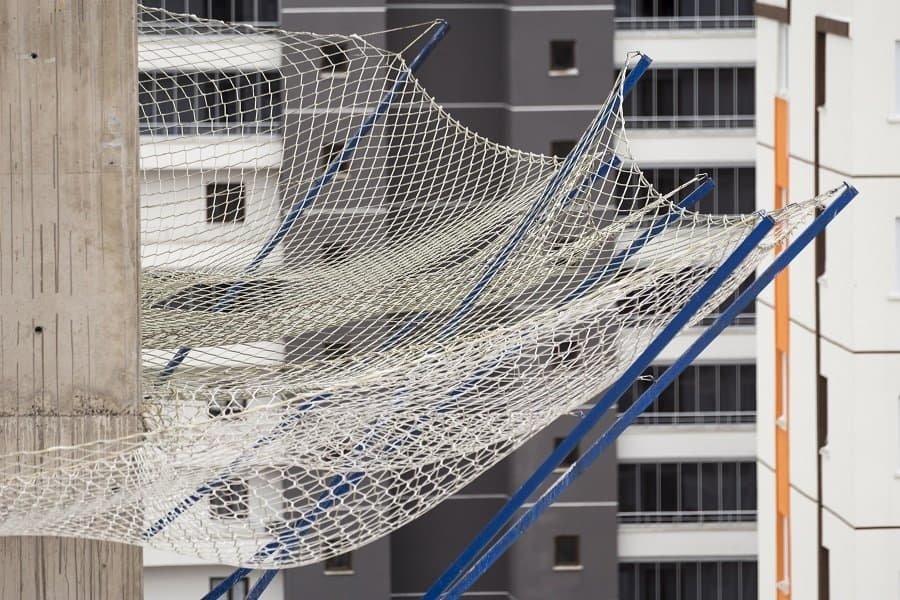



How to Install A Safety Net
Step 1: Develop a Solution Based on Site Assessment
Before installing safety nets, conduct a comprehensive assessment of the construction site. Identify potential fall hazards and heights to determine the type and quantity of safety nets required. Develop a thorough solution to address these hazards.
Step 2: Select and Prepare Anchor Points
Identify suitable anchor points for installing safety nets. Anchor points should be capable of bearing the intended loads and securely fastened to structural components. Inspect and ensure the structural integrity of anchor points. Install anchor devices such as eye bolts, clamps, or beam straps according to manufacturer specifications and industry standards.
Step 3: Install Safety Nets
Position safety nets horizontally below the work area, ensuring sufficient coverage and overlap to effectively catch falling workers or debris. Secure the safety nets to anchor points using appropriate attachment methods such as hooks, carabiners, or tie-off straps. Ensure proper tensioning of the safety nets to prevent sagging and maintain effectiveness in the event of a fall.
Considerations:
In general, the higher the fall height, the greater the impact force generated, and the more significant the deformation of the safety net. Therefore, when installing safety nets, it’s essential to leave sufficient clearance below the work area so that the safety nets can absorb the energy generated by the fall impact as much as possible. This prevents objects caught by the safety nets from hitting obstacles or the ground.

OSHA Safety Net requirements
OSHA regulations mandate that employers provide fall protection for employees when they face vertical drops of 6 feet or more. If employers opt for safety net systems, they must adhere to the following provisions:
- Safety nets should be installed as close to the working surface as possible to ensure employee safety. However, the installation height should not exceed 30 feet under any circumstances.
- When applying safety nets on bridges, ensure that potential fall areas remain clear to ensure safety.
- The mesh size of safety nets must not exceed 6 inches by 6 inches (15 centimeters).
- Border ropes must be securely attached to the safety net, with a diameter of at least 5/16 inches (0.8 centimeters).
- The entire net must extend outward from the outermost projection of the working surface.
Vertical distance from work plane to net level | Minimum horizontal distance required between the outer edge of the net and the edge of the working surface |
Up to 5 feet | 8 feet |
5 to 10 feet | 10 feet |
More than 10 feet | 13 feet |
- Regular inspections of safety nets should be conducted at least once a week, with documentation of inspection details such as time, personnel involved, and results. This ensures that relevant personnel are promptly informed of the safety net’s status.
- Ensure timely cleaning and disposal of all debris captured by safety nets.
These are some key requirements OSHA has outlined for safety nets in construction. For more specific information, please refer to the OSHA official website: https://www.osha.gov/etools/construction/falls/safety-net
Inspection & Maintenance of safety nets in construction
Typically, with proper maintenance, construction safety nets can be reused. Here are some maintenance suggestions:
- Employee Training: Train employees on how to correctly use and maintain safety nets, emphasizing their importance.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of safety nets for integrity, stability, and functionality. Pay particular attention to holes, tears, wear, or corrosion. Inspections should be carried out by qualified personnel trained in fall protection and safety net maintenance. Inspect safety nets before each use and regularly during construction projects.
- Avoid Overloading: Safety nets should not be overloaded to avoid exceeding their load-bearing capacity. If feasible, conduct periodic load testing of safety nets to ensure they can withstand expected loads and provide sufficient fall protection.
- Cleaning and Maintenance: Regularly clean safety nets to remove dust, dirt, and other contaminants that could impair their performance. For significant damage or structural issues, replace the affected parts or the entire safety net as needed.
- Proper Storage: Store safety nets properly when not in use to prevent damage and extend their lifespan. When not in use, store them in a dry, ventilated, and shaded area, away from direct sunlight and moisture.
Note: If safety nets are found to be damaged or no longer suitable for use, they should be replaced promptly.












